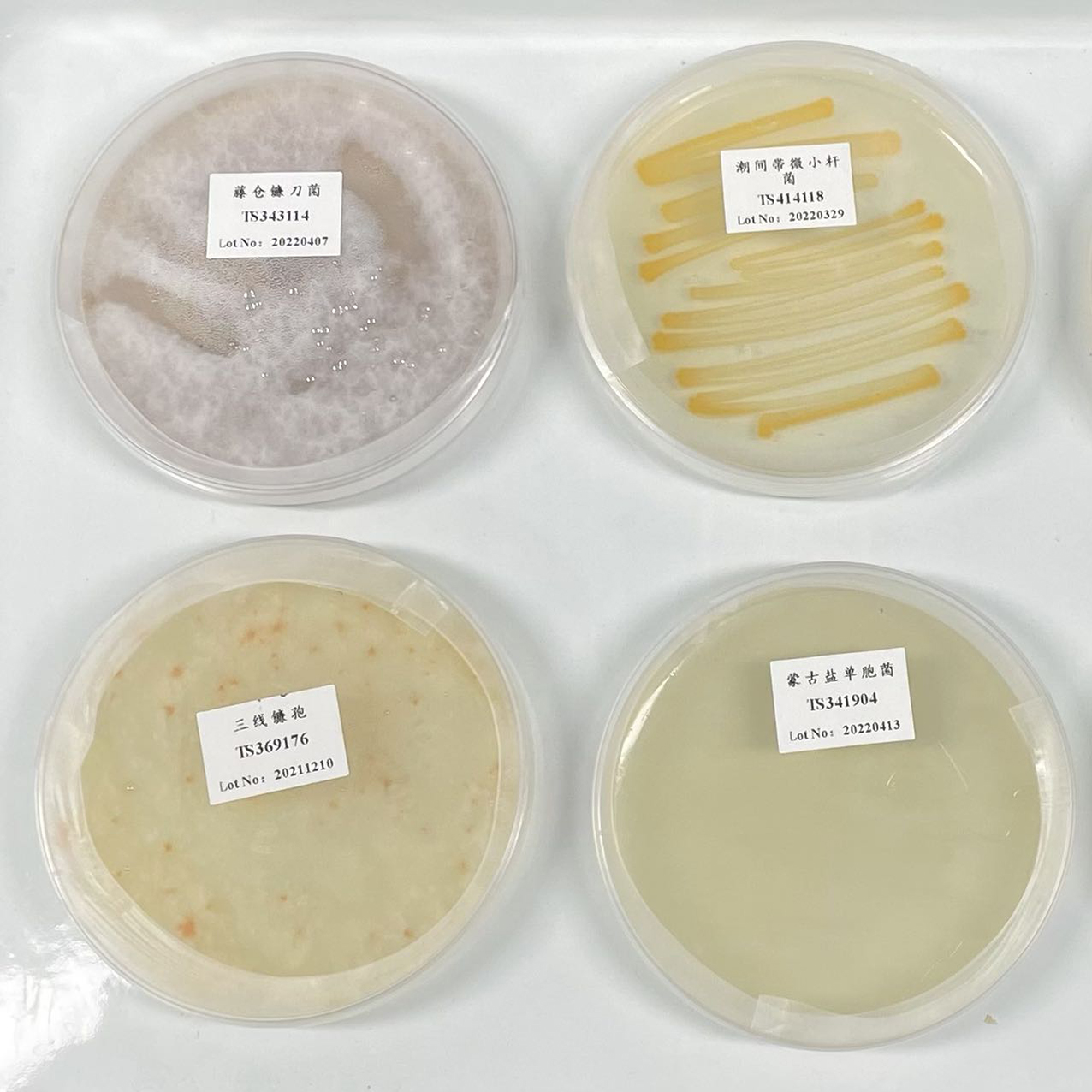
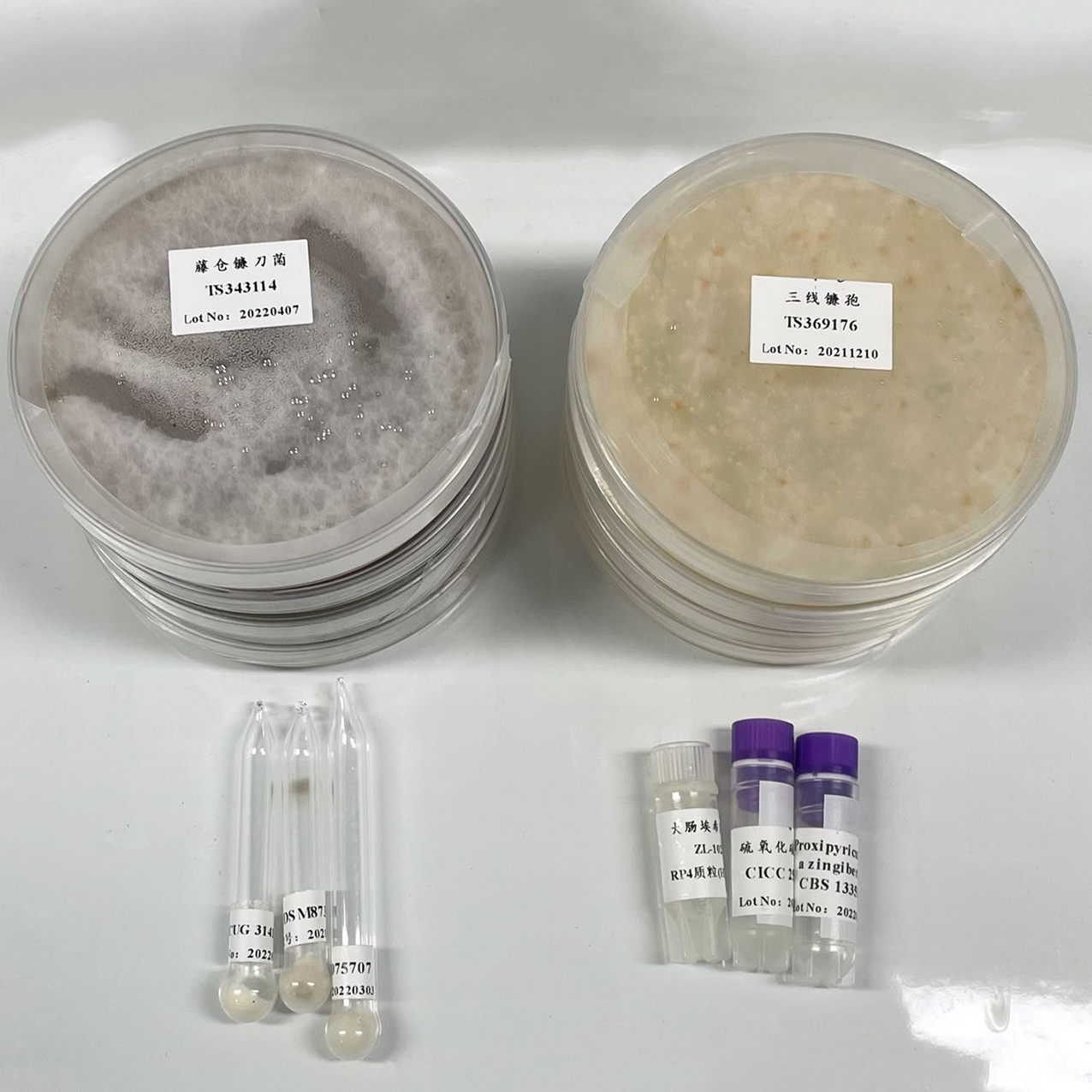
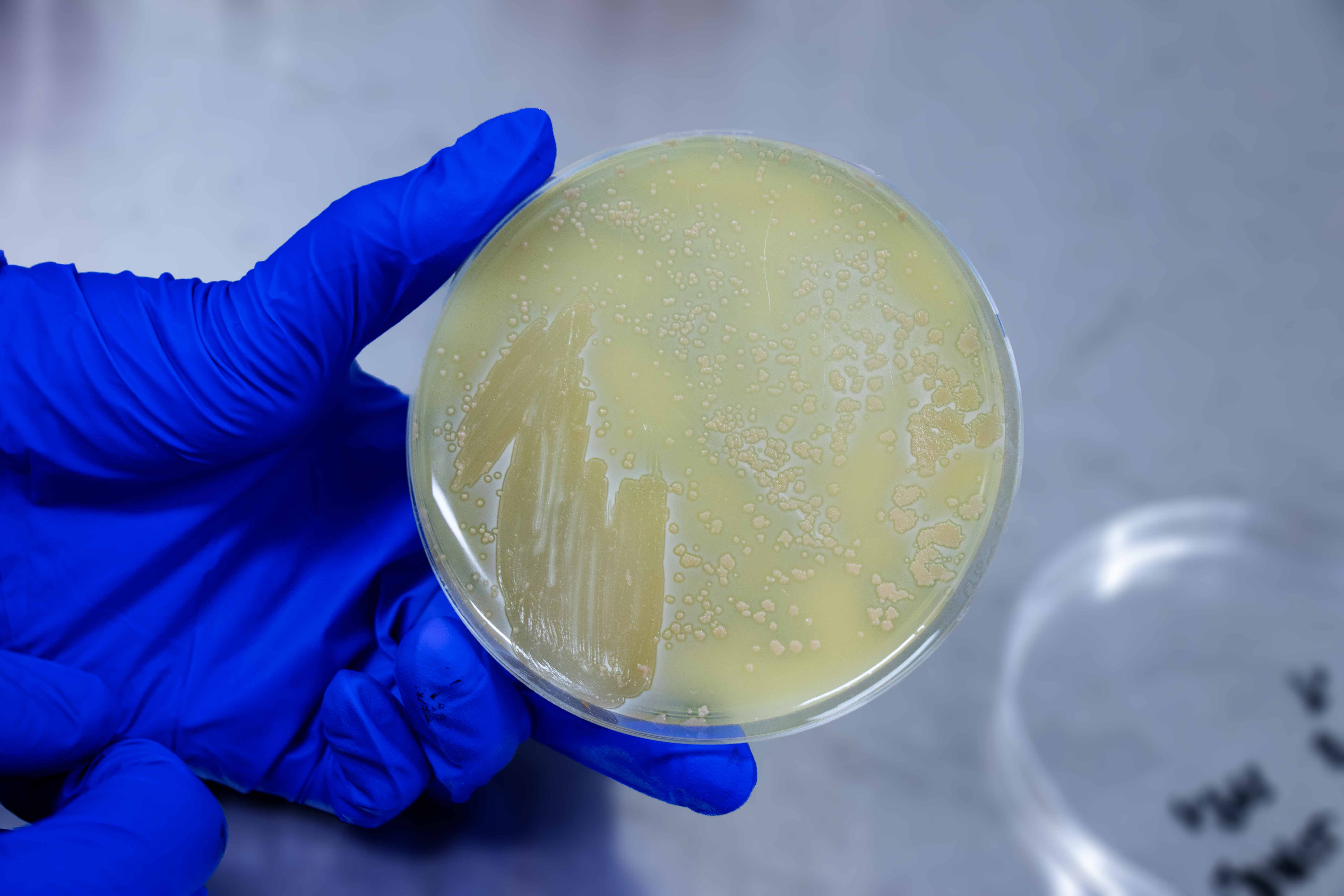
NCIMB 9109
NCIMB 9109
规格:
货期:
编号:TS391415
品牌:Testobio
| NCIMB number | NCIMB 9109 |
| Deposit type | Bacteria |
| Type strain | No |
| GMO | No |
| Taxon name | Escherichia coli |
| Depositor designation | Pfizer1965-108 |
| Preservation method | Lyophilised |
| Other catalogue information | Used with ESCHERICHIA COLI NCIMB 9110 in the production of lysine |
| Price band | A |
| Media | 001 |
| Gas regime | aerobic |
| Growth factors (and/or information) | NA, 37C, 24hr: metallic sheen, butyrous consistency, uniform suspension |
| ACDP category | 2 |
| Hazard information | This species has been associated with diarrhoea, urinary tract infections. |
| Colony Edge | Entire |
| Colony Surface | Smooth |
| Colony Shape | Circular |
| Colony Elevation | Low Convex |
| Colony Colour | Yellow-White |
| Colony Opacity | Opaque |
| Cellular Shape | Rod |
| Cellular Arrangement | Singly/Pairs |
| Cellular Motility | No |
| Gram stain | Gram Negative |
| Cellular (Other) | Straight Axis, Parallel Sides, Rounded Ends, Monomorphic, Motility + At 20C |
| Depositor Company | American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) |
| Depositor Address | 12301 Parklawn Drive Rockville Maryland 20852 U.S.A. |
| Date of Accession | 21/11/1961 |
| History | Chas. Pfizer Co. |
| Other collection IDs | ATCC12408 NCIMB9342 |
| Genotype information | lys |
| Yeast? | False |
| K12 | No |
| References | Casida L.E. Jr. (1956) US Patent 2,771,396 Preparation of Diaminopimelic Acid and Lysine. Prescott s.C. and Dunn C.G. (1959) Commercial Production of L-lysine. In "Industrial Microbiology" 3rd edition pp710-711 Bishop D.G. and Work E. (1965) Biochem J. 96 p567. An Extracellular Glycolipid produced by E. coli grown under Lysine limiting conditions. Taylor A., Knox K.W. and Work E. (1966) Biochem. J. 99 p53 Knox K.W. et al (1967) Biochem. J. 103 p192. An extracellular lipopolysaccharide phospholipid protein complex produced by E. coli grown under lysine limiting conditions. Damoglou A.P. and Dawes E.A. (1968) Biochem. J. 110 p775. Studies on the lipid content and phosphase requirement of glucose- and acetate- grown E. coli |
首页/产品中心/进口菌株
产品中心
联系我们 CONTACT US
0574-87917803
testobio@163.com
浙江省宁波市镇海区庄市街道兴庄路9号
创e慧谷42号楼B幢401室
最新促销
名称:NCIMB 8960
名称:NCIMB 8864
名称:NCIMB 9855
名称:NCIMB 9814
名称:NCIMB 9752
名称:NCIMB 9269
名称:NCIMB 8925
名称:NCIMB 8713
名称:NCIMB 8578
名称:NCIMB 8550
名称:NCIMB 9884
名称:NCIMB 8687

NCIMB 9109
NCIMB 9109
规格:
货期:
编号:TS391415
品牌:Testobio
标准菌株
定量菌液
DNA
RNA
规格:
冻干粉
斜面
甘油
平板
| NCIMB number | NCIMB 9109 |
| Deposit type | Bacteria |
| Type strain | No |
| GMO | No |
| Taxon name | Escherichia coli |
| Depositor designation | Pfizer1965-108 |
| Preservation method | Lyophilised |
| Other catalogue information | Used with ESCHERICHIA COLI NCIMB 9110 in the production of lysine |
| Price band | A |
| Media | 001 |
| Gas regime | aerobic |
| Growth factors (and/or information) | NA, 37C, 24hr: metallic sheen, butyrous consistency, uniform suspension |
| ACDP category | 2 |
| Hazard information | This species has been associated with diarrhoea, urinary tract infections. |
| Colony Edge | Entire |
| Colony Surface | Smooth |
| Colony Shape | Circular |
| Colony Elevation | Low Convex |
| Colony Colour | Yellow-White |
| Colony Opacity | Opaque |
| Cellular Shape | Rod |
| Cellular Arrangement | Singly/Pairs |
| Cellular Motility | No |
| Gram stain | Gram Negative |
| Cellular (Other) | Straight Axis, Parallel Sides, Rounded Ends, Monomorphic, Motility + At 20C |
| Depositor Company | American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) |
| Depositor Address | 12301 Parklawn Drive Rockville Maryland 20852 U.S.A. |
| Date of Accession | 21/11/1961 |
| History | Chas. Pfizer Co. |
| Other collection IDs | ATCC12408 NCIMB9342 |
| Genotype information | lys |
| Yeast? | False |
| K12 | No |
| References | Casida L.E. Jr. (1956) US Patent 2,771,396 Preparation of Diaminopimelic Acid and Lysine. Prescott s.C. and Dunn C.G. (1959) Commercial Production of L-lysine. In "Industrial Microbiology" 3rd edition pp710-711 Bishop D.G. and Work E. (1965) Biochem J. 96 p567. An Extracellular Glycolipid produced by E. coli grown under Lysine limiting conditions. Taylor A., Knox K.W. and Work E. (1966) Biochem. J. 99 p53 Knox K.W. et al (1967) Biochem. J. 103 p192. An extracellular lipopolysaccharide phospholipid protein complex produced by E. coli grown under lysine limiting conditions. Damoglou A.P. and Dawes E.A. (1968) Biochem. J. 110 p775. Studies on the lipid content and phosphase requirement of glucose- and acetate- grown E. coli |