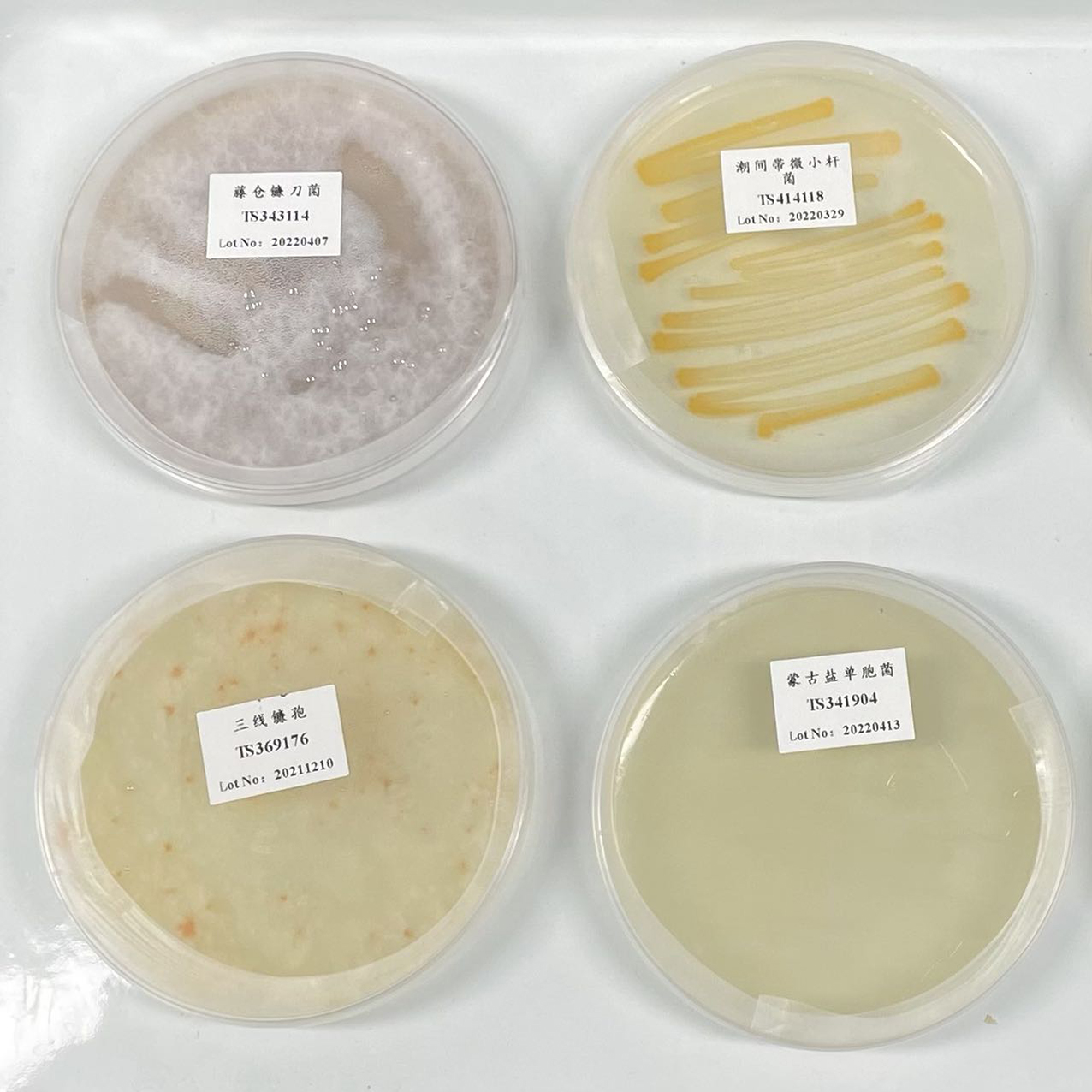
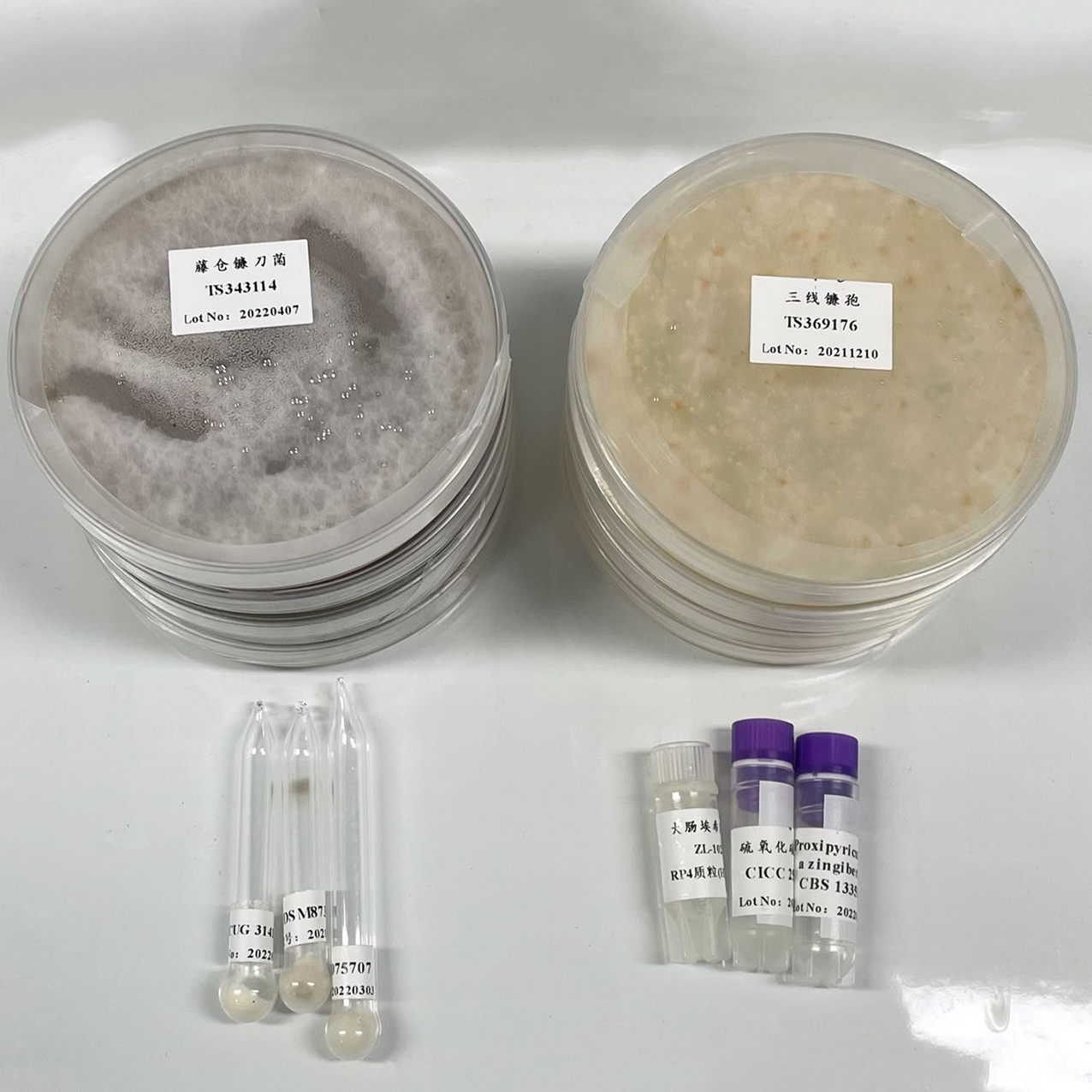
NCIMB 13542
NCIMB 13542
规格:
货期:
编号:TS391488
品牌:Testobio
| NCIMB number | NCIMB 13542 |
| Deposit type | Bacteria |
| Type strain | Yes |
| GMO | No |
| Taxon name | Haloarcula argentinensis |
| Depositor designation | arg-1 |
| Preservation method | Lyophilised |
| Other catalogue information | Extreme or obligately halophilic archaea |
| Price band | B |
| Media | 219 |
| Gas regime | aerobic |
| Incubation period | 7 days |
| Optimum pH (and/or range) | 7.5 |
| ACDP category | 1 |
| Colony Edge | Entire |
| Colony Surface | Smooth + Shiny |
| Colony Shape | Circular |
| Colony Elevation | Convex |
| Colony Colour | Orange-Red |
| Colony Opacity | Semi Transparent |
| Cellular Shape | Pleomorphic, Rods |
| Cellular Arrangement | Singly + Groups |
| Gram stain | Gram Negative |
| Depositor Company | Japanese Collection of Microorganisms (JCM) |
| Depositor Address | Hirosawa, Wako-shi Saitama 351-01 Japan |
| Source | Soils in Argentina salt flats |
| Isolated by | "Ihara, K" |
| Date of Accession | 06/11/1998 |
| Other collection IDs | JCM9737 |
| Yeast? | False |
| K12 | No |
| References | IJSB 1997, 47, 73-77 Arch. Biochem. Biophys (1994) 315, 127-132 Further refinement of the phylogeny of the Halobacteriaceae based on the full-length RNA polymerase subunit B (rpoB) gene, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(10), 2398-2408, 2010 Polyamine analysis of extremely halophilic archaebacteria, Ann Gunma Health Sci 19, 1-4, 1998 Gene orders in the upstream of 16S rRNA genes divide genera of the family Halobacteriaceae into two groups, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(1), 188-195, 2012 Haloarcula argentinensis sp. nov. and Haloarcula mukohataei sp. nov., two new extremely halophilic archaea collected in Argentina, Int J Syst Bacteriol 47(1), 73-77, 1997 The novel ion pump rhodopsins from Haloarcula from a family independent from both the bacteriorhodopsin and archaerhodopsin families/tribes, Arch Biochem Biophys 315, 127-132, 1994 Ureases of extreme halophiles of the genus Haloarcula with a unique structure of gene cluster, Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68(2), 397-406, 2004 |
首页/产品中心/进口菌株
产品中心
联系我们 CONTACT US
0574-87917803
testobio@163.com
浙江省宁波市镇海区庄市街道兴庄路9号
创e慧谷42号楼B幢401室
最新促销
名称:NCIMB 13561
名称:NCIMB 13559
名称:NCIMB 13554
名称:NCIMB 13555
名称:NCIMB 13550
名称:NCIMB 13532
名称:NCIMB 13547
名称:NCIMB 13545
名称:NCIMB 13536
名称:NCIMB 13535
名称:NCIMB 13510
名称:NCIMB 13509

NCIMB 13542
NCIMB 13542
规格:
货期:
编号:TS391488
品牌:Testobio
标准菌株
定量菌液
DNA
RNA
规格:
冻干粉
斜面
甘油
平板
| NCIMB number | NCIMB 13542 |
| Deposit type | Bacteria |
| Type strain | Yes |
| GMO | No |
| Taxon name | Haloarcula argentinensis |
| Depositor designation | arg-1 |
| Preservation method | Lyophilised |
| Other catalogue information | Extreme or obligately halophilic archaea |
| Price band | B |
| Media | 219 |
| Gas regime | aerobic |
| Incubation period | 7 days |
| Optimum pH (and/or range) | 7.5 |
| ACDP category | 1 |
| Colony Edge | Entire |
| Colony Surface | Smooth + Shiny |
| Colony Shape | Circular |
| Colony Elevation | Convex |
| Colony Colour | Orange-Red |
| Colony Opacity | Semi Transparent |
| Cellular Shape | Pleomorphic, Rods |
| Cellular Arrangement | Singly + Groups |
| Gram stain | Gram Negative |
| Depositor Company | Japanese Collection of Microorganisms (JCM) |
| Depositor Address | Hirosawa, Wako-shi Saitama 351-01 Japan |
| Source | Soils in Argentina salt flats |
| Isolated by | "Ihara, K" |
| Date of Accession | 06/11/1998 |
| Other collection IDs | JCM9737 |
| Yeast? | False |
| K12 | No |
| References | IJSB 1997, 47, 73-77 Arch. Biochem. Biophys (1994) 315, 127-132 Further refinement of the phylogeny of the Halobacteriaceae based on the full-length RNA polymerase subunit B (rpoB) gene, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(10), 2398-2408, 2010 Polyamine analysis of extremely halophilic archaebacteria, Ann Gunma Health Sci 19, 1-4, 1998 Gene orders in the upstream of 16S rRNA genes divide genera of the family Halobacteriaceae into two groups, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(1), 188-195, 2012 Haloarcula argentinensis sp. nov. and Haloarcula mukohataei sp. nov., two new extremely halophilic archaea collected in Argentina, Int J Syst Bacteriol 47(1), 73-77, 1997 The novel ion pump rhodopsins from Haloarcula from a family independent from both the bacteriorhodopsin and archaerhodopsin families/tribes, Arch Biochem Biophys 315, 127-132, 1994 Ureases of extreme halophiles of the genus Haloarcula with a unique structure of gene cluster, Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68(2), 397-406, 2004 |