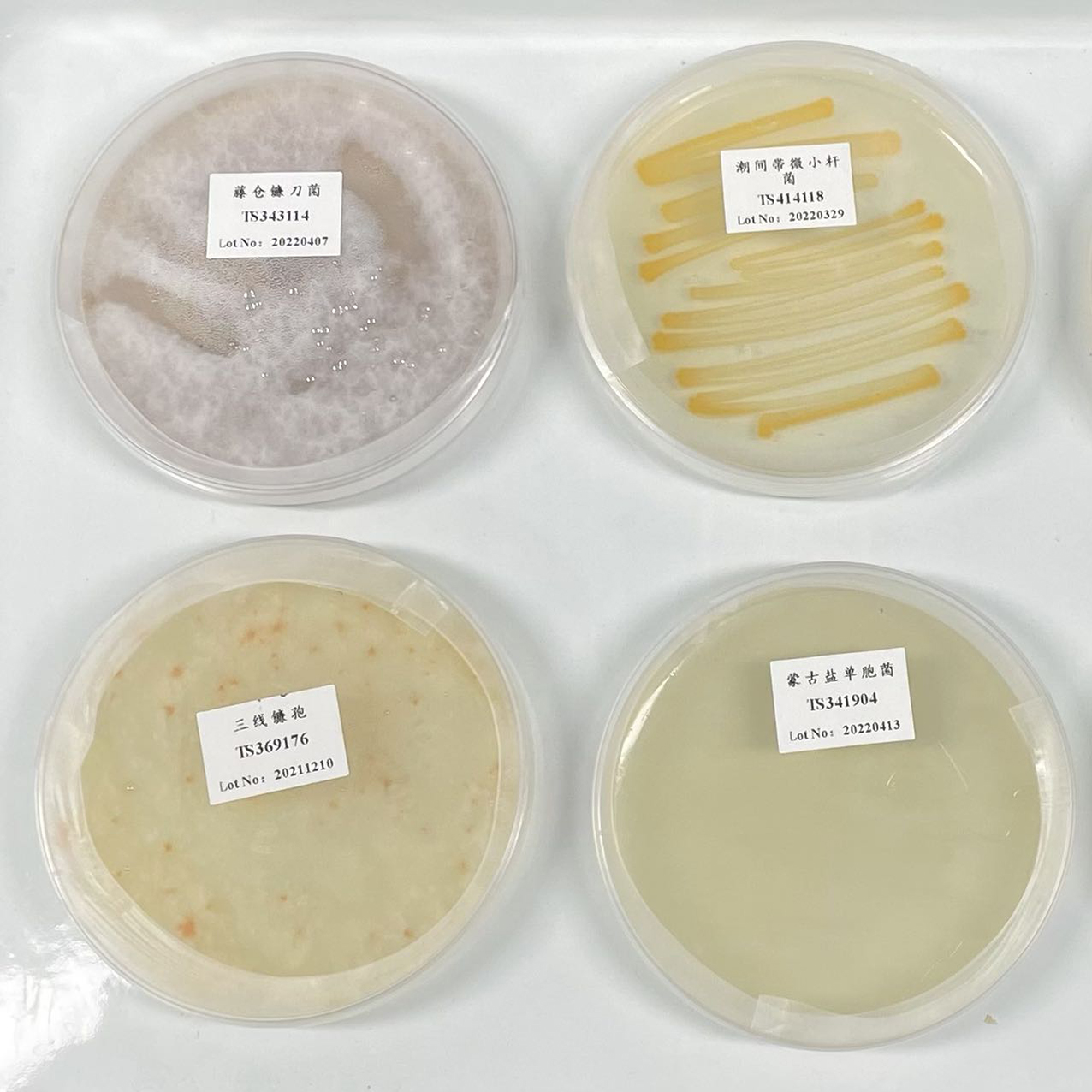
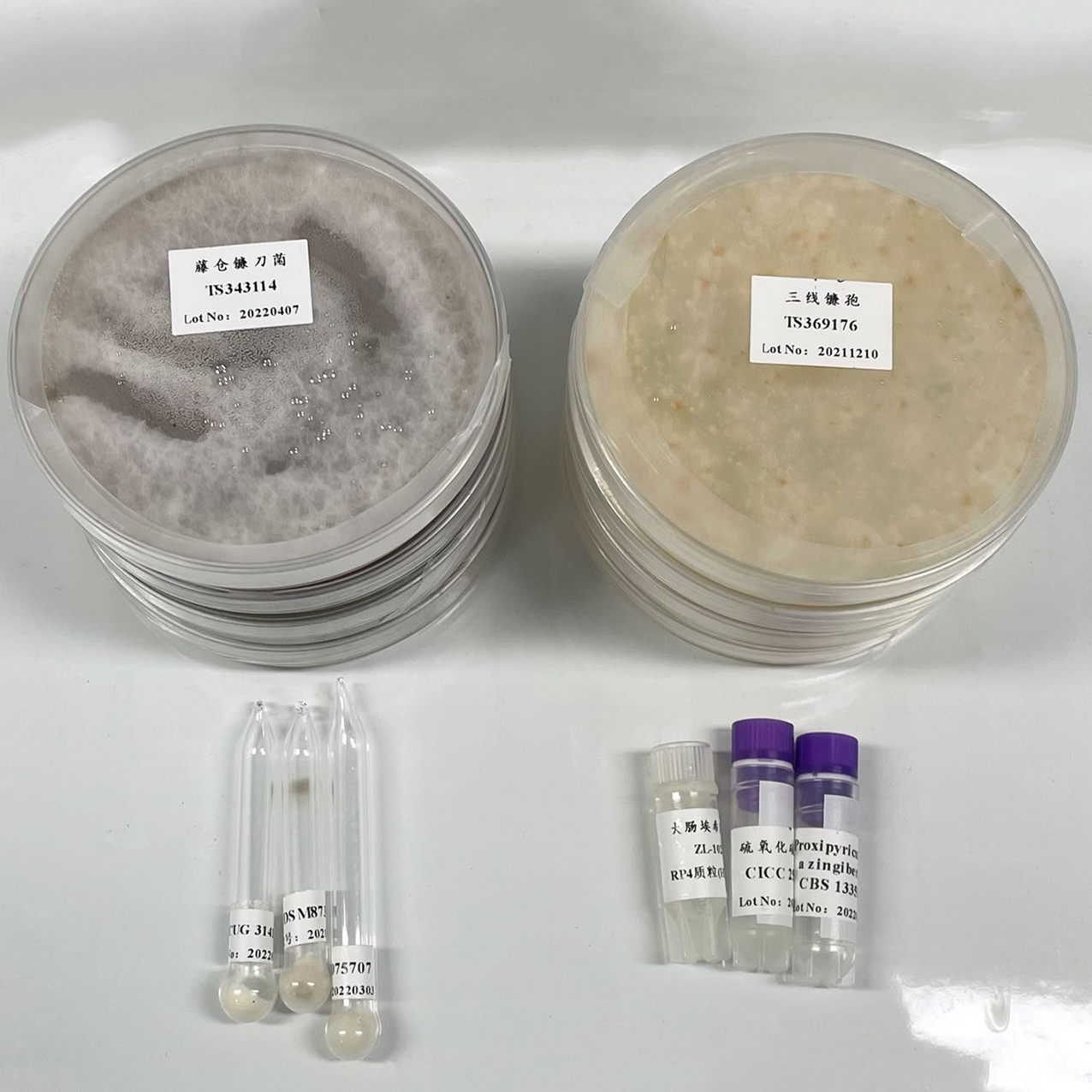
NCIMB 13707
NCIMB 13707
规格:
货期:
编号:TS391594
品牌:Testobio
| NCIMB number | NCIMB 13707 |
| Deposit type | Bacteria |
| Type strain | Yes |
| GMO | No |
| Taxon name | Xenophilus azovorans |
| Depositor designation | KF46F |
| Preservation method | Lyophilised |
| Price band | A |
| Media | 001 |
| Gas regime | aerobic |
| ACDP category | 1 |
| Colony Edge | Entire |
| Colony Shape | Circular |
| Colony Elevation | Convex |
| Colony Colour | Cream |
| Cellular Shape | Rod |
| Gram stain | Gram Negative |
| Depositor Name | Dr Andreas Stolz |
| Depositor Company | Institut fur Mikrobiologie der Universitat Stuttgart |
| Depositor Address | Allmandring 31 70569 Stuttgart Germany |
| Source | "Soil after continuous enrichment with 1-(4-caboxy-phenylazo)-2-naphthol, Switzerland" |
| Date of Isolation | 01/01/1980 |
| Date of Accession | 10/08/2000 |
| History | "Obtained from Prof Dr T Leisinger, ETH Zurich, Switzerland" |
| Other collection IDs | ATCCBAA-794 CCUG47268 DSM13620 |
| Yeast? | False |
| K12 | No |
| References | Zimmermann, T., F Gasser, H G Kulla & T Leisinger 1984 Comparison of two bacterial azoreductases acquired during adaptation to growth on azo dyes. Arch Microbiol. 138:37-43 Zimmermann, T., H.G. Kulla & T Leisinger, 1982. Properties of purified Orange II azoreductase, the enzyme initiating azo dye degradation by Pseudomonas KF46. Eur. J. Biochem. 129:197-203. Kulla, H.G., F. Klausener, U. Keyer, B. Ludeke & T Leisinger. 1983 Interference of aromatic sulfo groups in the microbial degradation of the azo dyes Orange I and Orange II. Arch. Microbiol. 135:1-7. Kulla, H.G., R. Krieg, T. Zimmermann & T Leisinger. 1984. Biodegradation of xenobiotics, experimental evolution of azo-dye degrading bacteria. In Current perspectives in microbial ecology (M.J. Klug & C A Reddy, eds). American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC. Blumel S et al (2001) IJSEM 51, 1831-1837 IJSEM (2003) 53:149 Biodegradation of xenobiotics, experimental evolution of azo-dye degrading bacteria.. In: Klug MJ , Reddy CA, editors. Current perspectives in microbial ecology. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology, (journal unknown) , 663-667, 1984 Comparison of two bacterial azoreductases acquired during adaptation to growth on azo dyes, Arch Microbiol 138(1), 37-43, 1984 Interference of aromatic sulfo groups in the microbial degradation of the azo dyes Orange I and Orange II, Arch Microbiol 135, 1-7, 1983 Properties of purified Orange II azoreductase, the enzyme initiating azo dye degradation by Pseudomonas KF46, Eur J Biochem 129(1), 197-203, 1982 Xenophilus azovorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a soil bacterium that is able to degrade azo dyes of the Orange II type, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(5), 1831-1837, 2001 |
首页/产品中心/进口菌株
产品中心
联系我们 CONTACT US
0574-87917803
testobio@163.com
浙江省宁波市镇海区庄市街道兴庄路9号
创e慧谷42号楼B幢401室
最新促销
名称:NCIMB 13696
名称:NCIMB 13706
名称:NCIMB 13654
名称:NCIMB 13683
名称:NCIMB 13682
名称:NCIMB 13681
名称:NCIMB 13680
名称:NCIMB 13679
名称:NCIMB 13677
名称:NCIMB 13671
名称:NCIMB 13670
名称:NCIMB 13636

NCIMB 13707
NCIMB 13707
规格:
货期:
编号:TS391594
品牌:Testobio
标准菌株
定量菌液
DNA
RNA
规格:
冻干粉
斜面
甘油
平板
| NCIMB number | NCIMB 13707 |
| Deposit type | Bacteria |
| Type strain | Yes |
| GMO | No |
| Taxon name | Xenophilus azovorans |
| Depositor designation | KF46F |
| Preservation method | Lyophilised |
| Price band | A |
| Media | 001 |
| Gas regime | aerobic |
| ACDP category | 1 |
| Colony Edge | Entire |
| Colony Shape | Circular |
| Colony Elevation | Convex |
| Colony Colour | Cream |
| Cellular Shape | Rod |
| Gram stain | Gram Negative |
| Depositor Name | Dr Andreas Stolz |
| Depositor Company | Institut fur Mikrobiologie der Universitat Stuttgart |
| Depositor Address | Allmandring 31 70569 Stuttgart Germany |
| Source | "Soil after continuous enrichment with 1-(4-caboxy-phenylazo)-2-naphthol, Switzerland" |
| Date of Isolation | 01/01/1980 |
| Date of Accession | 10/08/2000 |
| History | "Obtained from Prof Dr T Leisinger, ETH Zurich, Switzerland" |
| Other collection IDs | ATCCBAA-794 CCUG47268 DSM13620 |
| Yeast? | False |
| K12 | No |
| References | Zimmermann, T., F Gasser, H G Kulla & T Leisinger 1984 Comparison of two bacterial azoreductases acquired during adaptation to growth on azo dyes. Arch Microbiol. 138:37-43 Zimmermann, T., H.G. Kulla & T Leisinger, 1982. Properties of purified Orange II azoreductase, the enzyme initiating azo dye degradation by Pseudomonas KF46. Eur. J. Biochem. 129:197-203. Kulla, H.G., F. Klausener, U. Keyer, B. Ludeke & T Leisinger. 1983 Interference of aromatic sulfo groups in the microbial degradation of the azo dyes Orange I and Orange II. Arch. Microbiol. 135:1-7. Kulla, H.G., R. Krieg, T. Zimmermann & T Leisinger. 1984. Biodegradation of xenobiotics, experimental evolution of azo-dye degrading bacteria. In Current perspectives in microbial ecology (M.J. Klug & C A Reddy, eds). American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC. Blumel S et al (2001) IJSEM 51, 1831-1837 IJSEM (2003) 53:149 Biodegradation of xenobiotics, experimental evolution of azo-dye degrading bacteria.. In: Klug MJ , Reddy CA, editors. Current perspectives in microbial ecology. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology, (journal unknown) , 663-667, 1984 Comparison of two bacterial azoreductases acquired during adaptation to growth on azo dyes, Arch Microbiol 138(1), 37-43, 1984 Interference of aromatic sulfo groups in the microbial degradation of the azo dyes Orange I and Orange II, Arch Microbiol 135, 1-7, 1983 Properties of purified Orange II azoreductase, the enzyme initiating azo dye degradation by Pseudomonas KF46, Eur J Biochem 129(1), 197-203, 1982 Xenophilus azovorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a soil bacterium that is able to degrade azo dyes of the Orange II type, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(5), 1831-1837, 2001 |