NCIMB 13786
NCIMB 13786
规格:
货期:
编号:TS391685
品牌:Testobio
| NCIMB number | NCIMB 13786 |
| Deposit type | Bacteria |
| Type strain | Yes |
| GMO | No |
| Taxon name | Amycolatopsis sacchari |
| Depositor designation | K24 |
| Preservation method | Lyophilised |
| Price band | A |
| Media | 486 |
| Gas regime | aerobic |
| Incubation period | 3 days |
| ACDP category | 1 |
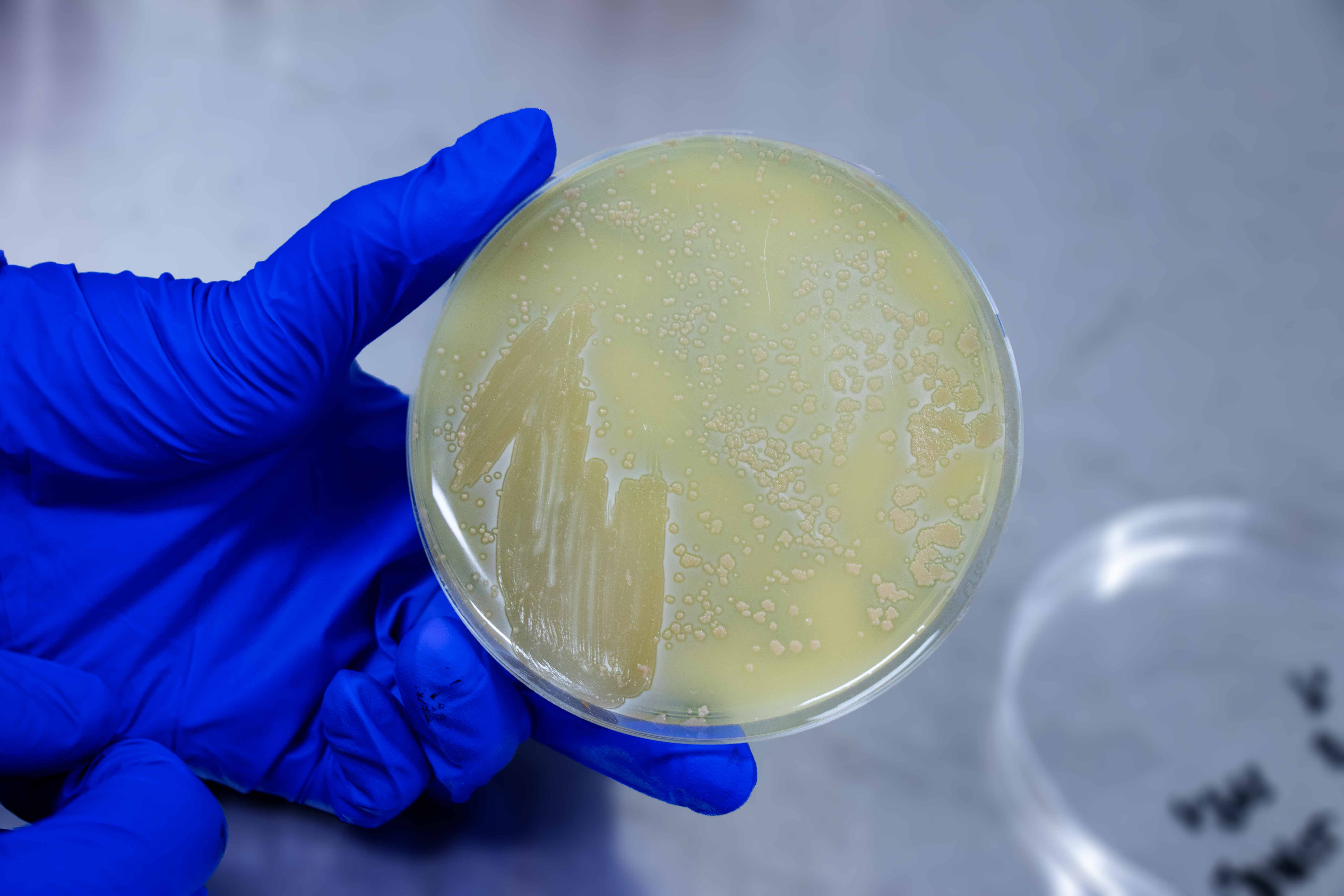
| Colony Edge | Irregular/Serrated |
| Colony Surface | Matt/Chalky |
| Colony Shape | Circular |
| Colony Elevation | Heaped |
| Colony Colour | Yellow |
| Colony Opacity | Opaque |
| Cellular Shape | Rod |
| Cellular Size | thin and long |
| Cellular Arrangement | Branching Filamentou |
| Gram stain | Gram Positive |
| Depositor Name | Michael Goodfellow |
| Depositor Company | University of Newcastle upon Tyne |
| Depositor Address | Department of Agricultural and Environmental Science Newcastle upon Tyne Tyne & Wear U.K. NE1 7RU |
| Source | "Sugar cane bagasse, floor dust, hemp factory, Lucknow, India" |
| Date of Accession | 10/04/2001 |
| History | J. Lacey (A1714) |
| Other collection IDs | "DSM 44468, KCTC 9863" |
| Yeast? | False |
| K12 | No |
| References | Amycolatopsis sacchari sp. nov a moderately thermophilic actinomycete isolated from vegetable matter, IJSEM (2001) 51, 187-193 Evaluation of the use of recN sequence analysis in the phylogeny of the genus Amycolatopsis; Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100(4), 21671192, 2011; , Amycolatopsis kentuckyensis sp. nov., Amycolatopsis lexingtonensis sp. nov. and Amycolatopsis pretoriensis sp. nov., isolated from equine placentas; Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(5), 1601-1605, 2003; , The use of gyrB sequence analysis in the phylogeny of the genus Amycolatopsis; Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 95(1), 1-11, 2009; , Amycolatopsis helveola sp. nov. and Amycolatopsis pigmentata sp. nov., isolated from soil; Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(11), 2629-2633, 2010; , Amycolatopsis sacchari sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic actinomycete isolated from vegetable matter; Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(1), 187-193, 2001; , Notification that new names and new combinations have appeared in volume 51, part 1, of the IJSEM; Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(2), 269, 2001; , |
首页/产品中心/进口菌株
产品中心
联系我们 CONTACT US
0574-87917803
testobio@163.com
浙江省宁波市镇海区庄市街道兴庄路9号
创e慧谷42号楼B幢401室
最新促销
名称:NCIMB 13797
名称:NCIMB 13798
名称:NCIMB 13780
名称:NCIMB 13656
名称:NCIMB 13655
名称:NCIMB 13699
名称:NCIMB 13705
名称:NCIMB 13698
名称:NCIMB 13700
名称:NCIMB 701986
名称:NCIMB 13792
名称:NCIMB 13647

NCIMB 13786
NCIMB 13786
规格:
货期:
编号:TS391685
品牌:Testobio
标准菌株
定量菌液
DNA
RNA
规格:
冻干粉
斜面
甘油
平板
| NCIMB number | NCIMB 13786 |
| Deposit type | Bacteria |
| Type strain | Yes |
| GMO | No |
| Taxon name | Amycolatopsis sacchari |
| Depositor designation | K24 |
| Preservation method | Lyophilised |
| Price band | A |
| Media | 486 |
| Gas regime | aerobic |
| Incubation period | 3 days |
| ACDP category | 1 |
| Colony Edge | Irregular/Serrated |
| Colony Surface | Matt/Chalky |
| Colony Shape | Circular |
| Colony Elevation | Heaped |
| Colony Colour | Yellow |
| Colony Opacity | Opaque |
| Cellular Shape | Rod |
| Cellular Size | thin and long |
| Cellular Arrangement | Branching Filamentou |
| Gram stain | Gram Positive |
| Depositor Name | Michael Goodfellow |
| Depositor Company | University of Newcastle upon Tyne |
| Depositor Address | Department of Agricultural and Environmental Science Newcastle upon Tyne Tyne & Wear U.K. NE1 7RU |
| Source | "Sugar cane bagasse, floor dust, hemp factory, Lucknow, India" |
| Date of Accession | 10/04/2001 |
| History | J. Lacey (A1714) |
| Other collection IDs | "DSM 44468, KCTC 9863" |
| Yeast? | False |
| K12 | No |
| References | Amycolatopsis sacchari sp. nov a moderately thermophilic actinomycete isolated from vegetable matter, IJSEM (2001) 51, 187-193 Evaluation of the use of recN sequence analysis in the phylogeny of the genus Amycolatopsis; Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100(4), 21671192, 2011; , Amycolatopsis kentuckyensis sp. nov., Amycolatopsis lexingtonensis sp. nov. and Amycolatopsis pretoriensis sp. nov., isolated from equine placentas; Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(5), 1601-1605, 2003; , The use of gyrB sequence analysis in the phylogeny of the genus Amycolatopsis; Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 95(1), 1-11, 2009; , Amycolatopsis helveola sp. nov. and Amycolatopsis pigmentata sp. nov., isolated from soil; Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(11), 2629-2633, 2010; , Amycolatopsis sacchari sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic actinomycete isolated from vegetable matter; Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(1), 187-193, 2001; , Notification that new names and new combinations have appeared in volume 51, part 1, of the IJSEM; Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(2), 269, 2001; , |